Table of Contents
ToggleDiabetes: What is it?
Diabetes is a condition brought on by an excessive rise in blood glucose levels. Glucose, often known as blood sugar, is the primary energy source in the body. Although glucose can be produced by your body, it can also be present in food.
The pancreas secretes the hormone insulin, which facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells for energy production. When you have diabetes, your body either produces insufficient amounts of insulin or uses it improperly. After that, the glucose does not enter your cells; instead, it stays in your blood.
Diabetes raises the risk of heart, kidney, nerve, and eye damage. There is a connection between diabetes and some cancers. You can lower your risk of developing diabetes-related health issues by managing or preventing diabetes.
Which kinds of diabetes are there?
Type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes are the three most prevalent forms of the disease.
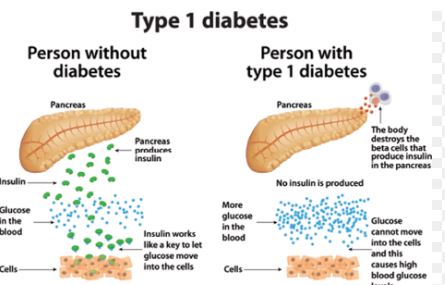
Diabetes Type 1
You have little to no insulin produced by your body if you have type 1 diabetes. The cells in your pancreas that produce insulin are attacked and destroyed by your immune system. Although it can manifest at any age, type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and young people. Insulin must be taken daily by people with type 1 diabetes in order to survive.
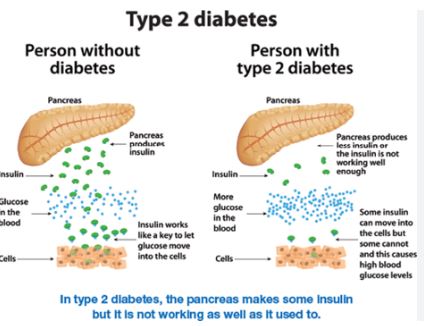
Type 2 diabetes
Insulin is not adequately utilised by the cells in your body if you have type 2 diabetes. Although the pancreas is capable of producing insulin, it does not produce enough of it to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Diabetes type 2 is the most prevalent kind of disease. If you have a family history of type 2 diabetes and other risk factors, such as being overweight or obese, your chances of developing the condition increase. Type 2 diabetes can strike at any age, even in early childhood.
Understanding the risk factors for type 2 diabetes and making healthy lifestyle choices, such as reducing weight or not gaining it, can help avoid the disease.
Pregnancy-related diabetes
One kind of diabetes that appears during pregnancy is called gestational diabetes. After the baby is born, this kind of diabetes usually disappears. On the other hand, type 2 diabetes is more likely to strike you later in life if you have gestational diabetes. Type 2 diabetes can occasionally be diagnosed as a pregnancy-related condition.
Prediabetes:
A person’s blood sugar levels are higher than normal in prediabetes, but not high enough to be classified as having type 2 diabetes. You are more likely to acquire type 2 diabetes in the future if you have prediabetes. In comparison to persons with normal glucose levels, you also have an increased risk of heart disease.
What is the prevalence of diabetes?
Diabetes is widespread. About 11% of the population in the US, or 37.3 million people, suffer from diabetes. Of all diabetes cases, type 2 diabetes accounts for 90% to 95% of cases.
Worldwide, 537 million adults suffer with diabetes. Experts predict that by 2030, there will be 643 million, and by 2045, there will be 783 million.
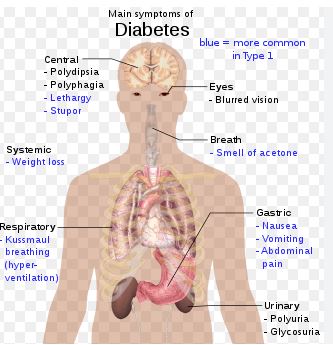
What signs of diabetes are present?
Diabetes symptoms include:
Dry tongue and increased thirst (polydipsia).
A lot of urine production.
Fatigue.
Vision blurry.
Unaccounted-for weight loss.
Tingling or numbness in your feet or hands.
Gradual recovery of a cut or wound.
Recurring yeast infections on the skin or in the vagina.
Diabetes: What causes it?
Any form of diabetes is brought on by an excess of glucose in the bloodstream. However, the type of diabetes you have will determine why your blood sugar level rises.
Diabetes has several causes, including
Insulin resistance:
Insulin resistance is the primary cause of type 2 diabetes. When your muscle, fat, and liver cells don’t react to insulin as they should, you develop insulin resistance. Insulin resistance can be caused by a wide range of illnesses and circumstances, including heredity, nutrition, physical inactivity, obesity, hormone imbalances, and some drugs.
Autoimmune diseases:
Your immune system attacking the cells in your pancreas that produce insulin causes Type 1 diabetes and LADA.
Hormonal imbalance:
The placenta releases hormones that lead to insulin resistance throughout pregnancy. Gestational diabetes may occur if your pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to combat insulin resistance. Cushing’s syndrome and acromegaly are two other hormone-related disorders that can lead to type 2 diabetes.
Pancreas damage:
Your pancreas’s capacity to produce insulin may be hampered by physical damage, such as that caused by an illness, surgery, or injury. This could lead to type 3C diabetes.
Genetic mutations: Certain genetic mutations have the potential to cause neonatal diabetes and MODY.
Long-term usage of some medications, such as corticosteroids and HIV/AIDS therapies, can also lead to type 2 diabetes.
What consequences might diabetes cause?
Diabetes can cause both short-term (transient and severe) and long-term problems, primarily as a result of abnormally high or persistently elevated blood sugar levels.
severe effects from diabetes
Among the potentially fatal consequences of acute diabetes are:
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic condition (HHS):
Individuals with type 2 diabetes are primarily susceptible to this consequence. This results in severe dehydration and confusion when your blood sugar level stays excessively high (more than 600 mg/dL) for an extended period of time. This needs to be treated medically right now.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA):
Individuals with type 1 diabetes or undiagnosed T1D are primarily susceptible to this consequence. When your body doesn’t have enough insulin, this occurs. Your body burns down fat when it lacks insulin, which prevents it from using glucose for energy. Your blood becomes acidic due to molecules called ketones that are eventually released during this process. This results in vomiting, unconsciousness, and breathing difficulties. DKA needs to be treated medically right away.
Hypoglycemia, or extremely low blood sugar, is the result of results that fall below what is considered healthy for you. Extremely low blood sugar is known as severe hypoglycemia. It primarily affects insulin-using diabetics.
Individuals with type 2 diabetes are primarily susceptible to this consequence. This results in severe dehydration and confusion when your blood sugar level stays excessively high (more than 600 mg/dL) for an extended period. This needs to be treated medically right now.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA):
Individuals with type 1 diabetes or undiagnosed T1D are primarily susceptible to this consequence. When your body doesn’t have enough insulin, this occurs. Your body burns down fat when it lacks insulin, which prevents it from using glucose for energy. Your blood becomes acidic due to molecules called ketones that are eventually released during this process. This results in vomiting, unconsciousness, and breathing difficulties. DKA needs to be treated medically right away.
Hypoglycemia, or extremely low blood sugar, is the result of a blood sugar level that falls below what is considered healthy for you. Extremely low blood sugar is known as severe hypoglycemia. It primarily affects insulin-using diabetics. Double or blurred vision, clumsiness, confusion, and convulsions are some of the symptoms. This need for immediate glucagon therapy or other medical attention.Diabetes Treatment
- Diabetes Treatment
Type 1 diabetics must take insulin on a regular basis to help control their blood sugar levels, even though there is no cure for the disease.
In addition, there are other oral antibiotic medications that may be useful in slowing the advancement of type 2 diabetes. Enhancing these steps can help you protect your health and successfully manage your diabetes.
In summary, diabetes is a serious condition, but it is also treatable. A balanced diet, frequent exercise, and a healthy lifestyle can all help regulate this illness. If you experience diabetes symptoms as well, see your doctor right away and receive the necessary care.
We are accountable for your well-being, so please take good care of yourself!
